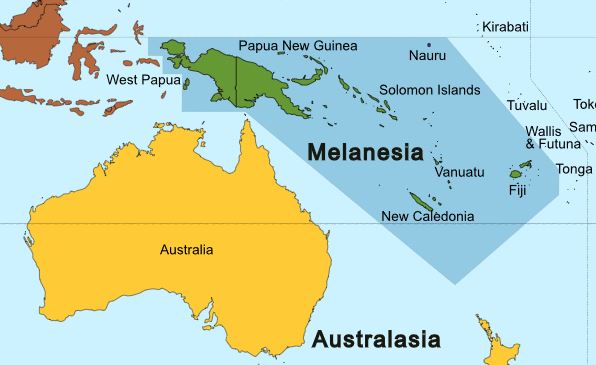
Melanesia, a region comprising Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, New Caledonia, and Fiji, is home to diverse and vibrant cultures. Over the years, numerous notable individuals from Melanesian ethnicity have gained recognition for their contributions to various fields. Here are 10 of the most popular celebrities and notable people from Melanesian heritage:
- Russell Crowe: A prominent actor, director, and producer, Russell Crowe rose to international fame for his role as the Roman general Maximus Decimus Meridius in the epic historical drama film “Gladiator.” His Melanesian heritage comes from Papua New Guinea.
- Jonah Lomu: Regarded as one of the greatest rugby players of all time, Jonah Lomu made a significant impact on the sport during his career with the New Zealand national team. His powerful running and exceptional athleticism earned him worldwide recognition.
- Israel Folau: A former professional rugby league and rugby union player, Israel Folau represented both Australia and Tonga on the international stage. Known for his speed, strength, and try-scoring ability, Folau made a name for himself in both codes of rugby.
- George Speight: A former Fijian military officer, George Speight gained notoriety for leading a military coup in Fiji in 2000. His actions resulted in a political crisis and the abdication of the President, Ratu Sir Kamisese Mara. Speight was later convicted and imprisoned for his role in the coup.
- Kevin Rudd: A former Prime Minister of Australia, Kevin Rudd served from 2007 to 2010 and again from 2013 to 2014. He is of mixed European and Melanesian ancestry, with his mother being from Papua New Guinea. Rudd is known for his progressive policies, particularly in the area of climate change.
- Eddie Nketiah: A talented footballer, Eddie Nketiah currently plays as a striker for Arsenal Football Club in the English Premier League. Born to Ghanaian parents in England, Nketiah identifies with his Melanesian heritage through his paternal grandmother, who is from Papua New Guinea.
- Bernard Narokobi: A renowned Papua New Guinean academic, politician, and poet, Bernard Narokobi made significant contributions to the development of his country. He served as a member of the Papua New Guinea National Parliament and is known for his advocacy for indigenous rights and cultural preservation.
- John Akii-Bua: A Ugandan athlete of Melanesian descent, John Akii-Bua made history by winning the gold medal in the 400-meter hurdles at the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich, Germany. His victory marked the first time an African athlete had won an Olympic gold medal in a track and field event.
- Rickie Lambert: A former English footballer, Rickie Lambert represented several clubs throughout his career, including Southampton, Liverpool, and West Ham United. Despite being born in England, Lambert has Melanesian heritage through his grandparents, who immigrated from the Solomon Islands.
- Nancy Wake: Born in New Zealand to a Scottish father and a Māori mother, Nancy Wake was a renowned resistance fighter during World War II. Known as the “White Mouse,” she served as a British Special Operations Executive agent in France and was instrumental in assisting Allied forces during the war.
Most Famous Melanesian People
Melanesian Mystique: Unraveling Three Key Historical Legacies
The Melanesian community is a diverse group of peoples inhabiting the islands of the southwestern Pacific Ocean. With a rich and complex history, Melanesia is home to numerous indigenous cultures that have left a lasting impact on the region and the world. From unique art forms to traditional belief systems, here are three of the most well-known historical inheritances associated with the Melanesian heritage.
1. Vibrant Artistic Traditions
One of the most notable aspects of the Melanesian heritage is its vibrant artistic traditions. Melanesian art is characterized by its intricate designs, bold colors, and skilled craftsmanship. From intricately carved sculptures to beautifully woven textiles, Melanesian artists have created a wide range of visually stunning pieces. These art forms often depict mythological figures, religious symbols, and scenes from everyday life.
- Woodcarving: Melanesian woodcarving is renowned for its intricate details and elaborate designs. Sculptures and masks carved from wood are commonly used in traditional rituals and ceremonies.
- Body Art: The tradition of body art is significant in Melanesian culture. Body painting and tattooing are used to convey social status, spiritual beliefs, and cultural identity.
- Textiles: Melanesian textiles, such as woven mats and bark cloth, are highly valued for their beauty and craftsmanship. These textiles often feature geometric patterns and motifs that hold cultural and symbolic meanings.
2. Rich Oral Traditions
Oral traditions play a crucial role in preserving the history and cultural heritage of Melanesian communities. Through storytelling, songs, and chants, the knowledge and wisdom of past generations are passed down to younger ones. These oral traditions often convey myths, legends, historical events, and moral lessons. They provide a deep understanding of Melanesian cultural values and belief systems.
- Mythology: Melanesian mythology is a fascinating blend of creation stories, supernatural beings, and ancestral spirits. These myths explain the origin of the universe, natural phenomena, and the relationships between humans and the spirit world.
- Folksongs: Traditional folksongs are an integral part of Melanesian oral traditions. These songs reflect various aspects of life, including love, nature, and daily activities. They are often accompanied by traditional musical instruments.
- Oratory: The art of oratory is highly regarded in Melanesian cultures. Skilled speakers are revered for their ability to convey complex ideas, pass down wisdom, and inspire community members through their words.
3. Spirituality and Ancestral Beliefs
The Melanesian heritage is deeply intertwined with spirituality and ancestral beliefs. Traditional religious practices, often known as animism, recognize the presence of spirits in the natural world and the importance of ancestral connections. These beliefs shape various aspects of Melanesian life, from daily rituals to social structures.
- Kastom: Kastom, a word derived from the English term “custom,” refers to the traditional practices and beliefs of Melanesian communities. These include rituals, ceremonies, and customary laws that govern social interactions and relationships.
- Ancestor Worship: Ancestor worship is a central aspect of Melanesian spirituality. It involves honoring and seeking guidance from deceased family members and ancestors, who are believed to play a role in the lives of the living.
- Sacred Sites: Melanesian communities have sacred sites, such as mountains, trees, and bodies of water. These places are considered spiritually significant and are often associated with specific rituals and ceremonies.
The Melanesian heritage is a treasure trove of cultural diversity, artistic expressions, and spiritual beliefs. It continues to thrive through the efforts of the communities and individuals who carry forward these traditions and values.
In a striking celebration of diversity, numerous prominent individuals proudly reflect a mosaic of Itaukei, Poland and Nordic roots, highlighting the intricate interplay of cultures within their heritage. From accomplished leaders to acclaimed artists, these figures embody the rich lexical semantic tapestry of ethnic backgrounds, illustrating the vibrant spectrum of human experiences.
Factsheet About Melanesian People
| Country | Population | Percentage of Total Population |
|---|---|---|
| Papua New Guinea | 8,084,991 | 85% |
| Solomon Islands | 686,884 | 95% |
| Vanuatu | 307,815 | 98% |
| Fiji | 936,387 | 83% |
| New Caledonia | 271,407 | 39% |
| Santa Cruz Islands (Solomon Islands) | 24,235 | 100% |
| West Papua (Indonesia) | 4,276,114 | 65% |

The Ancient Heritage of Melanesian Ethnic Groups
Melanesian Ethnicity: References and Resources
The Melanesian ethnic group is a diverse collection of indigenous people inhabiting the region of Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. This region includes several countries such as Papua New Guinea, Fiji, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, and New Caledonia. If you are interested in learning more about the Melanesian ethnic group, here are some references and resources to help you dig deeper:
-
Books:
- “Melanesia: Beyond Diversity” by Robert W. Williamson – This book offers an insightful exploration of the cultural, social, and political dynamics within Melanesia.
- “The Power of Perspective: The Austronesian Political Thought of Fijian Chiefs” by Julie Peteet – This book examines the political thought of Fijian chiefs and provides an understanding of Fijian society.
- “The Languages of Melanesia: A Bibliographic Guide” by Mervyn C. Alleyne – This comprehensive guide offers a wealth of information on the diverse languages spoken in Melanesia.
-
Academic Articles:
- “Understanding Melanesians: An Overview of Socio-Cultural Issues in Melanesia” – This article by Derek A. Fee provides an overview of the socio-cultural issues faced by Melanesian societies, including kinship systems, cultural rituals, and inter-ethnic relations.
- “Melanesian Cultural Heritage: A Comprehensive Review” by Paul Munro and Ian Lilley – This article explores the rich cultural heritage of Melanesia, including its art, music, dance, and traditional knowledge systems.
-
Museums and Cultural Centers:
- National Museum and Art Gallery of Papua New Guinea – Located in Port Moresby, the capital of Papua New Guinea, this museum showcases a rich collection of artifacts, artworks, and cultural exhibits from Melanesian cultures.
- Fiji Museum – Situated in Suva, the capital of Fiji, this museum houses a diverse range of cultural artifacts representing the historical and contemporary aspects of Fijian and Melanesian cultures.
- Solomon Islands National Museum – Located in Honiara, the capital of the Solomon Islands, this museum features exhibitions on the history, culture, and natural heritage of the islands.
-
Online Resources:
- Virtual Museum of Melanesia – This online resource provides a virtual tour of Melanesian artifacts and collections, offering an opportunity to explore the cultural diversity of the region from the comfort of your own home.
- Encyclopedia of World Cultures: Melanesians and Their Culture – This comprehensive online encyclopedia entry delves into various aspects of Melanesian culture, including language, religion, social organization, and traditional practices.
- The Melanesian Journal of Theology – This online journal provides academic articles and research papers exploring theological reflections within the context of Melanesian cultures.
These references and resources will provide you with valuable insights into the Melanesian ethnic group and help you gain a deeper understanding of their cultures, languages, and traditions.
As we continue to celebrate diversity and embrace the richness of different cultures, let us honor and draw inspiration from these remarkable individuals who have shaped our world. Thank you for joining us on this captivating journey.



Companies That Support Israel: A List to Avoid
Does Red Bull Support Israel? Decoding the Unraveled Connection
Boycott List: Fashion Companies Supporting Israel You Should Be Aware Of
The 15 Biggest Woolworths Supermarkets in Sydney
Does These Firearms Support Israel? Exploring the Unraveled Connection
Does These Tech Brands Support Israel? Decoding the Unraveled Connection
Does These Filmography Support Israel? Understanding the Intricate Ties
Does These Online Business Support Israel? Exploring the Unraveled Connection